What Does the Kinetic Molecular Theory Describe
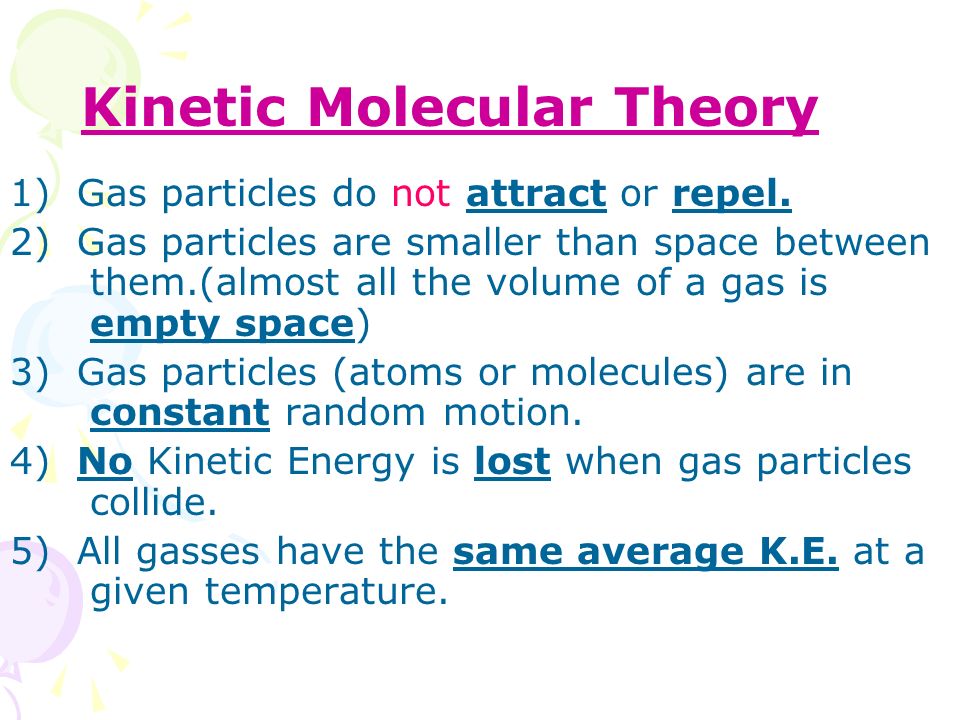
Describe the liquid state according to the kinetic-molecular theory. The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Postulate 2 zGas molecules are in constant random straight line motion with varying velocities.
Kinetic Molecular Theory Ppt Video Online Download
Definite volume but indefinite shape.

. That gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions. This model is used to describe the behavior of gases. This model is used to describe the behavior of gases.
What does the kinetic theory describe. More specifically it is used to explain macroscopic properties of a gas such as pressure and temperature in terms of its microscopic components such as atoms. Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions.
Like the ideal gas law this theory was. The kinetic molecular theory of matter offers a description of the microscopic properties of atoms or molecules and their interactions leading to observable macroscopic properties such as pressure volume temperature. The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior.
What is the theory used to explain changes in state. The basics of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases KMT should be understood. Properties of liquids include.
The energy of atomic orbitals C. The kinetic-molecular theory describes why gases are more compressible than either liquids or solids. Describe the particle motion of solids liquids and gases.
The Kinetic Molecular theory is used to describe the behavior of gas. Review Questions Answer KEY 1. The kinetic-molecular theory explains the physical properties of solids liquids and gases in terms of the energy of particles and the A.
The kinetic molecular theory states that the motion of molecules is predictable based upon measurable traits such as the temperature volume and pressure of the atmosphere. Kinetic Molecular Theory can be used to explain both Charles and Boyles Laws. Gay-Lussacs Law states that in a closed system of fixed volume as the temperature of a gas increases the pressure increases as well.
Gases are compressible due to the fact that the majority of the volume of a gas is made up of the big quantities of void in between the gas particles. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance or. The Kinetic Molecular theory is used to describe the behavior of gas.
Kinetic Molecular Theory states. The transfer of atoms in reactions B. It gives the relationship between pressure temperature and kinetic energy.
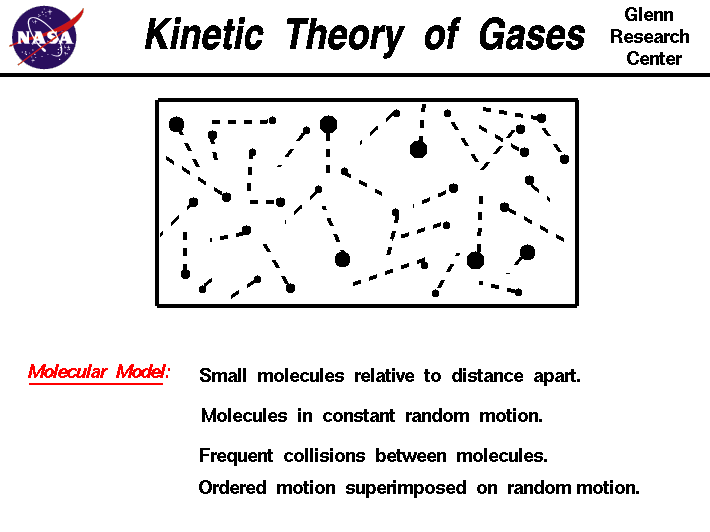
Kinetic molecular theory kmt worksheet answer key Kinetic Molecular Theory Worksheet. The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their absolute. A regular spacing or arrangement of atomsmolecules within a crystal.
The basics of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases KMT should be understood. Kinetic Molecular Theory can be used to explain both Charles and Boyles Laws. Of or relating to motion.
Proof - Brownian motion displays molecular motion. The gaseous molecules are in constant random motion. This can be explained using kinetic molecular theory or how the movement of individual gas particles affects the behavior of a gas as a whole.
What does the Kinetic Molecular Theory State. Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions. Theory of treating samples of matter as a large number of small particles atoms or molecules all of which are in constant random motion.
The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to absolute temperature only. According to the kinetic-molecular theory of liquids the particles are not bound together in fixed positions. What is the theory used to explain changes in state.
More specifically it is used to explain macroscopic properties of a gas such as pressure and temperature in terms of its microscopic components such as atoms. Describe the 3 assumptions of the KNIT Kinetic Molecular Theory. Instead they move about constantly giving them their fluidity.
Use the following terms to fill in the blanks. Fluidity of the particles. It gives the relationship between pressure temperature and kinetic energy.
CHAPTER 12 GASES AND KINETIC-MOLECULAR THEORY The kinetic molecular theory of gases is a model that helps us understand the physical properties of gases at the. The reactivity of valence electrons D. The Kinetic Molecular Theory KMT is a model used to explain the behavior of matter.
The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to absolute temperature only. The mass of the particles.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Fiveable
No comments for "What Does the Kinetic Molecular Theory Describe"
Post a Comment